hypermobility in babies ankles
If the sensitivity to stretch is very low the muscles are slow to respond and they appear to be weak and floppy. As she got older she would sit in the w position and sleep with her legs in the same position shes now 7 and has problems running her feet ankles and hips are turning and we.

What Is Hypermobility In Babies Children Young Adults Therapy Stars
The pain is more common in the legs such as the calf or thigh muscles.
. However some children have a condition called Joint Hypermobility Syndrome or JHS. Bend a little finger back more than 90 degrees. While standing put hands flat on floor while knees stay straight.
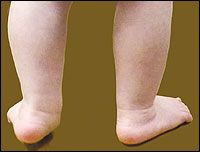
In infants with joint hypermobility the connective tissue that holds the muscles together and connects the muscles to the bones via the tendons is very pliable. Hypermobility in the joints of the feet and ankles may cause the feet to roll in giving an excessively flat-footed appearance. Unstable ankles and overly flexible.
The term benign hypermobility joint syndrome BHJS is a common source of joint or muscle complaints that often cause concern for parents children and school personnel. The term benign hypermobility joint syndrome BHJS is a common source of joint or muscle complaints that often cause concern for parents children and school personnel. This is an advantage to some children and tends to be.
Joint hypermobility and musculoskeletal injury. Sensible footwear choices are extremely important and simple changes here can make a significant difference to many people with hypermobility. It is not unusual to have a few hypermobile joints.
Children or young adults with hypermobility have joint pain. Joint hypermobility without pain occurs when children have stretchy or flexible joints but without exercise-related pain. Rarely mild joint swelling may come.
This happens when the connective tissue which makes up the joint. Infants with joint hypermobility have joints that are able to bend further than usual and a trunk and limbs that appear to be floppy and weak. Being extremely flexible and having pain associated with this flexibility could indicate that your child is hypermobile.
It might affect the fingers and hands. Joint hypermobility in babies and children is even more common and usually. Joint mobility is highest at birth there is a decrease in children around nine to twelve years old.
For most children hypermobility affects just the joints. For most children hypermobility affects just the joints. Joint hypermobility happens most often in children and reduces with age.
It most often involves large joints such as the knees or elbows. In most people this causes no problems and does not require treatment. Foot and ankle complaints are common in people with hypermobility.
Joint hypermobility can differ between individuals. A short video clip from Podiatrist Andrew Bull a member of our health professional network on foot ankle pronation and hypermobility. In addition to hypermobile joints a child with JHS.
This can be very common in children 10-15 and usually decreases with age. In infants with joint hypermobility the connective tissue that holds the. It is sometimes referred to as being double jointed and is quite common about 1 in 10 people are hypermobile.
Bend a thumb backwards to touch your forearm. It is well recognized that many if not most children and adolescents attending paediatric rheumatology clinics will have a non-inflammatory origin for their complaints or disorder. Most people with hypermobility will not find a genetic cause but early identification means that steps can be taken to minimise injury.
Hypermobility in the joints of the feet and ankles may cause the feet to roll in giving an excessively flat-footed appearance. Foot Ankle Pronation in Hypermobility. The term generalised joint hypermobility GJH is used when a child has several joints that are more flexible than usual.
The ability of a joint to move beyond its normal range of motion is joint hypermobility. Joint mobility is highest at birth there is a. As children with hypermobile joints require added support around the heel and ankle the shoes should have a closed solid and ideally high heel cap.
However in some people hypermobile joints can cause joint pain and result in higher rates of. The increased range of movement at the joints. Hypermobility can be associated with recurrent pains at the end of the day or at night in the knees feet andor ankles.
Children with hypermobility Beighton score 49 were recruited for a longitudinal study from The Childrens. One way to check if the.

My Child Is Very Flexible Is This Normal Sole Motion Podiatry
Physiotherapy For Children Provided By Kidsphysio In Milton Keynes Bedford Flitwick Ampthill Hypermobility

Could My Baby Have Hypermobility

Hypotonia Why Milestones Are Harder For My Third Baby Cando Kiddo Hypotonia Hypotonia Baby Baby Workout

Hypermobility Syndrome Therapies For Kids

Orthotic Management Of Low Tone Children The Earlier The Better The O P Edge Magazine
Physiotherapy For Children Provided By Kidsphysio In Milton Keynes Bedford Flitwick Ampthill Foot And Ankle Conditions

How To Recognise Joint Hypermobility In Your Child My Strong Little Body

Treatment For Flat Feet Therapies For Kids

How Hypermobility And Low Muscle Tone Affect Your Baby S Development Skills For Action
Hypermobility Syndromes Children Arthritis Australia

How Hypermobility And Low Muscle Tone Affect Your Baby S Development Skills For Action

The Best Shoes For Kids With Hypermobility Extra Arch And Ankle Support Fitting Children S Shoes

What Is Hypermobility In Babies Children Young Adults Therapy Stars

Hypermobility In Children The Real Deal Youtube

How Hypermobility And Low Muscle Tone Affect Your Infant S Development Low Muscle Tone Pediatric Physical Therapy Muscle Tone
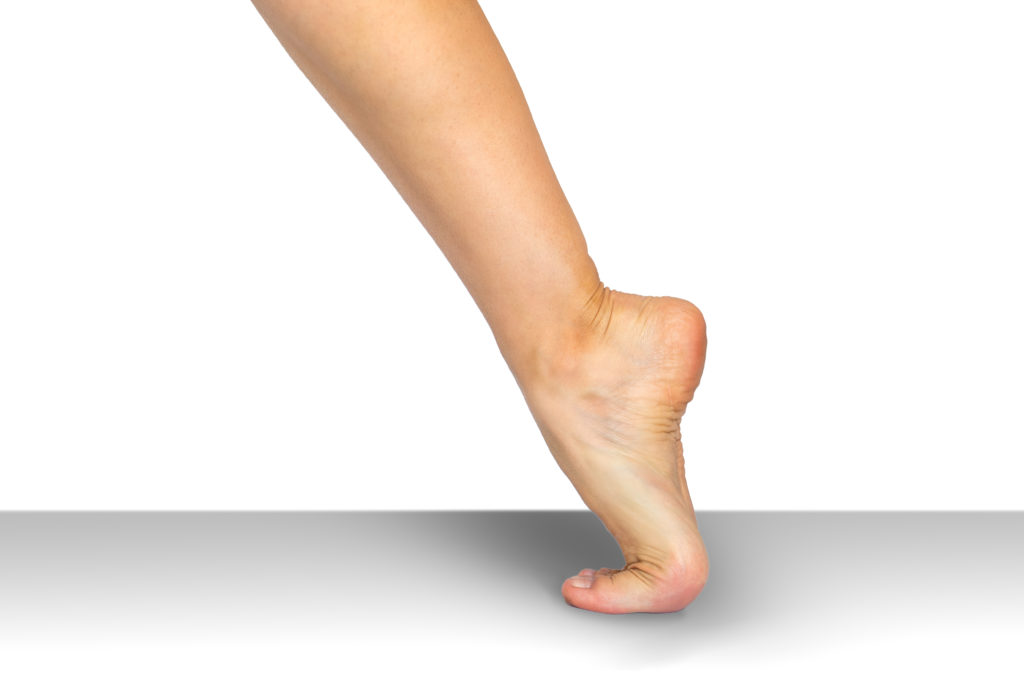
Joint Hypermobility Kids Adults My Footdr

When To Brace Kids With Low Muscle Tone And Pronation Surestep

How Hypermobility And Low Muscle Tone Affect Your Baby S Development Skills For Action